Future outlook#
Some improvements can be made to pySailingVLM to decrease the time execution of the program.
GPU#
Apart form CPU programing, Numba library supports CUDA GPU programming. The library allows to directly compile a restricted subset of Python code into CUDA kernels and device functions using the CUDA execution model. Kernels which are written in Numba appear to have direct access to NumPy arrays according to documantation [num]. The NumPy arrays are automatically shifted between the CPU and the GPU. To further increase performance of the code, pySailingVLM can be ported to GPU.
All code as SoA#
Up to now, most of the data structures in pySailingVLM are represented as Structure of Arrays, except panels. To take full adventage of vectorization, the panels shall be also rewriten into SoA layout. This memory layout is especially recommended for CUDA acceleration [WP16] due to parallel access to data units.
Points dupllicate#
Panels which are close to each other share same points (see Figure 25). Current pySailingVLM implementation (legacy from OO implementation) does not take into account this fact and there are duplicates of points coordinates in the panel array. Reducing redundant points can improve memory consumption and code efficiency.
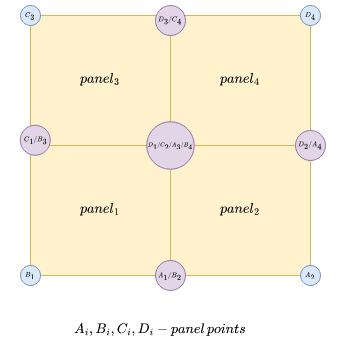
Fig. 25 Points on panels arragement. Figure created by author.#
Adjoint optimization#
The adjoint formulation for the pySailingVLM has been derived analytically. The formulation is intented to accelarete the sail shape optimization in order to find the best design for given wind conditions. If you are interested in collaboration and further development of the pySailingVLM package please contact the authors (GGruszczynski).